The Zero-Admin Meeting Lifecycle
This system monitors Google Calendar to automate the entire meeting lifecycle, instantly generating standardized Google Docs and initiating follow-up tracking.
Difficulty
Intermediate
Time Required
15-25 hours
Technologies
7 Tools
Project managers spent 10-15 minutes before every meeting manually creating, formatting, and sharing documentation, leading to significant administrative waste and reduced profitability.
A Google Apps Script (GAS) powered system was deployed to instantly generate and share standardized meeting documentation, eliminating 100% of manual preparation.
The agency achieved consistent documentation across all projects and drastically improved follow-up accountability, eliminating manual meeting preparation time.
Automation Case Study: The Zero-Admin Meeting Lifecycle
Zero-Admin Meetings: GAS-Powered Lifecycle Management
2. Overview
This system, designed for high-velocity Google Workspace environments, monitors Google Calendar to automate the entire meeting lifecycle. It instantly generates standardized Google Docs (pre-populated with agenda, attendees, and context), shares them, and initiates follow-up tracking.
This deployment eliminated 100% of manual meeting preparation, ensuring consistent documentation across all projects and drastically improving follow-up accountability within the Marketing Agency environment.
3. The Challenge: The Cost of Manual Prep
Marketing Agencies bill staff time hourly, making administrative waste a direct hit to profitability. The traditional process of managing meeting documentation created critical pain points:
- Time Sink: Project managers spent 10-15 minutes before every meeting manually creating, formatting, and sharing documentation. With 30-40 meetings per team per week, this amounted to 5-10 hours of non-billable, repetitive setup time weekly.
- Inconsistency: Varied note formats made data retrieval—specifically finding key decisions or tracking past action items—a time-consuming audit across disorganized Drive folders.
- Context Loss: Critical details (final attendee list, original meeting description, video conference links) were often missed or incorrectly copied from the calendar event.
- Follow-up Failure: Action items lacked a systematic reminder or tracking system. Without a centralized trigger, tasks were dropped, leading to missed deadlines and accountability issues.
- High Volume: The sheer volume of meetings meant quality control on documentation was the first thing sacrificed under pressure.
4. The Solution: Orchestrating Google Workspace
The solution uses Google Apps Script (GAS) as the middleware to orchestrate Google Calendar, Google Docs, and Gmail. The system runs on a time-driven trigger, identifying newly tagged meetings and executing the full workflow in under 30 seconds.
ROI Snapshot: By automating a 10-minute task that occurred 30 times a week, we saved the agency 5 hours weekly per team. At an average staff cost of $40/hour, this automation generates $200+ in weekly value, delivering full ROI on the deployment cost in under 30 days.
Core Components:
- Google Apps Script: Logic, API calls, and scheduling engine.
- Google Calendar: Source of truth for meeting metadata.
- Google Docs: Destination for the formatted, standardized notes template.
- Google Drive / Advanced Drive Service: Structured storage for enterprise-grade Shared Drive compatibility.
5. Implementation: Battle-Tested Architecture
5.1 Prerequisites and Technical Stack
- Active Google Workspace Domain.
- A designated Google Drive folder for storing notes. (Note: If this folder is on a Shared Drive, the Advanced Drive Service must be enabled and used for file operations.)
- A pre-formatted Google Docs template ('Master Template') with specific text placeholders (e.g.,
{{MEETING_TITLE}}). - Google Apps Script Project running the automation.
- Necessary GAS services enabled:
Calendar Service,Drive Service,Document Service,Gmail Service. (Correction: For robust enterprise deployment, the Advanced Drive Service should be enabled to ensure compatibility with Shared Drives.)
5.2 Architecture Diagram (Text-Based)
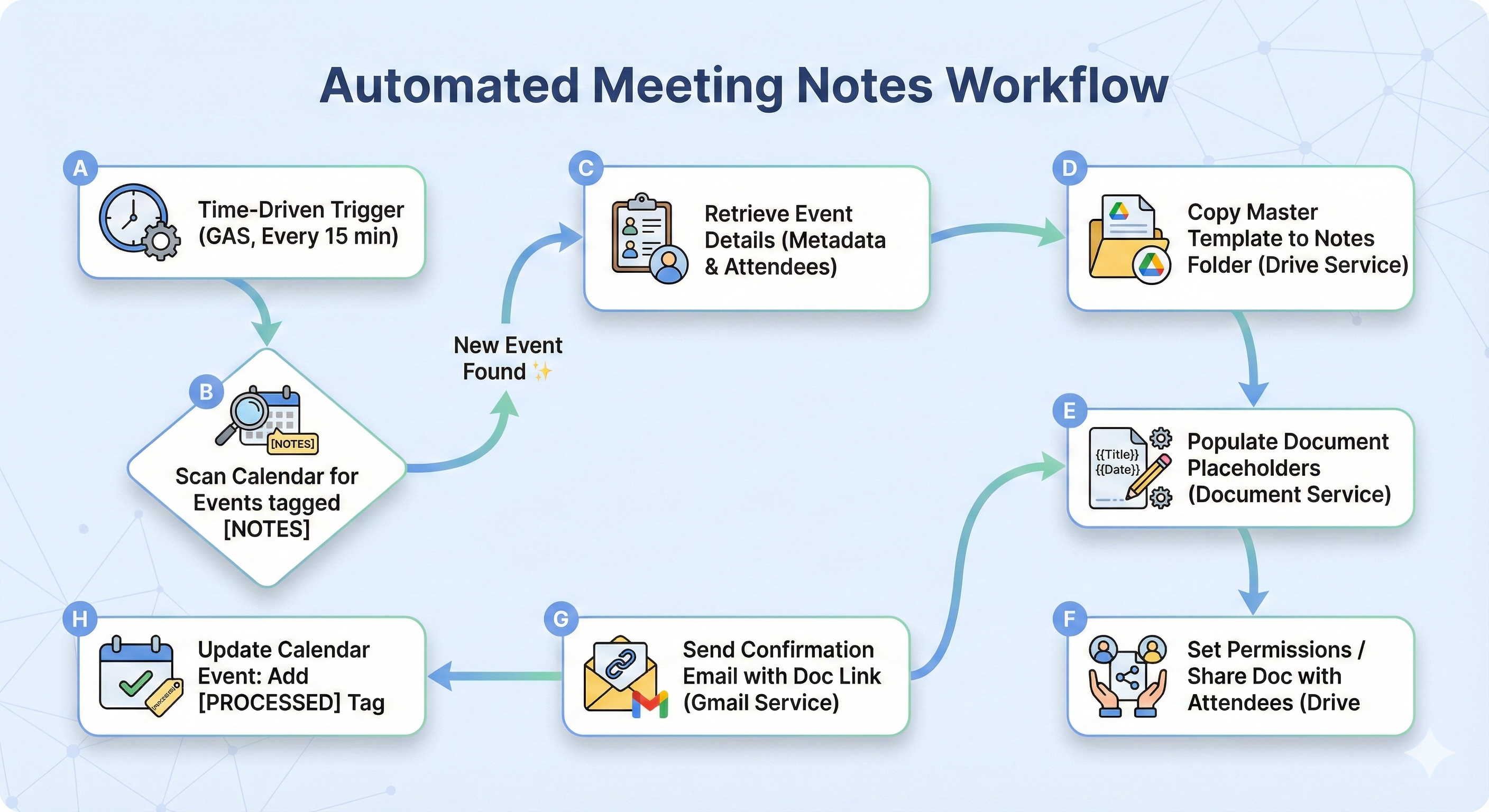
5.3 Core Script Logic
Step 5.3.1: Setting Up the Master Template
Placeholders use unique characters (double curly braces) for reliable script replacement.
| Placeholder | Replacement Value |
|---|---|
{{MEETING_TITLE}} |
Event title |
{{DATE_TIME}} |
Formatted start and end time |
{{ATTENDEE_LIST}} |
Bulleted list of participant emails |
{{MEETING_CONTEXT}} |
Original calendar event description |
Step 5.3.2: The Main Script Logic (Code.gs)
This function defines configuration, sets the scanning window, and implements the critical duplication prevention check ([PROCESSED] tag).
// Pseudo code for the application
CONSTANTS: CALENDAR_ID, TEMPLATE_ID, FOLDER_ID, TAG
FUNCTION processNewMeetings
GET Meetings in next 4 hours
FOR EACH Meeting:
IF Tagged AND Not Processed:
TRY
CALL generateNotesDocument(Meeting)
MARK Meeting as Processed
CATCH Error
LOG Error
END FUNCTIONStep 5.3.3: Document Generation and Population
This function handles copying the template, extracting data, and performing text replacement.
// Pseudo code for the application
FUNCTION generateNotesDocument(event)
GET Meeting Details (Title, Time, Attendees, Context)
// File Creation
COPY Template -> "Notes - {Title} - {Date}"
// Population
OPEN Copy
REPLACE Placeholders:
{{MEETING_TITLE}} -> Title
{{ATTENDEE_LIST}} -> Attendees
{{MEETING_CONTEXT}} -> Context
SAVE and CLOSE
// Sharing
CALL shareAndNotify(NewFile, Attendees, Title)
END FUNCTIONStep 5.3.4: Sharing and Notification
This step ensures immediate accessibility and informs participants via email.
// Pseudo code for the application
FUNCTION shareAndNotify(file, attendees, title)
// Permissions
FOR EACH Attendee:
GRANT Editor Access
// Notification
SEND Email to Attendees
SUBJECT: "Notes Ready: {Title}"
BODY: "Use this link: {URL}"
END FUNCTION5.4 Testing Checklist
| Test Case | Expected Result | Pass/Fail | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| T1: Trigger Deployment | Time-driven trigger is set to run every 15 minutes. | ||
| T8: Duplication Prevention | The calendar event description is updated with [PROCESSED], and subsequent script runs do not create duplicate documents. |
||
| T6: Sharing Permissions | All invited attendees receive Editor access to the new document. | ||
| T7: Email Notification | Attendees receive the confirmation email containing the correct document URL. |
5.5 Troubleshooting Section
| Problem | Potential Cause | Resolution |
|---|---|---|
| Script runs but fails to create documents. | The script owner lacks permission to access the folder. (Technical Note: If the folder is a Shared Drive, the script must use the Advanced Drive Service.) | Verify IDs are correct. Ensure the script owner has "Owner" or "Editor" access to the template and destination folder. |
| Placeholders are replaced with garbage characters. | The template used a rich-text element that interferes with simple replaceText(). |
Ensure placeholders are simple text strings. (Optimization: For complex templates, migrate to the Docs API batchUpdate method.) |
| Duplicate documents are being created. | The event.setDescription(...) command is failing silently, or the [PROCESSED] tag check is flawed. |
Check the Calendar event description manually after the first run. Check GAS logs for permission errors when modifying the calendar event. |
6. Advanced Enhancements: Accountability and Scaling
These enhancements move the system from simple generation to managing the full accountability lifecycle.
-
Action Item Tracker Integration (High ROI): Enforce accountability by extracting action items and pushing them into a central tracking sheet.
- Method: Users tag action items in the Google Doc using a uniform format (e.g.,
[ACTION] Task description @assignee #duedate). - Script Logic: A secondary GAS function runs daily, searches generated notes for the
[ACTION]regex pattern, parses the data, and appends a new row to a master Google Sheet (The Action Item Tracker).
- Method: Users tag action items in the Google Doc using a uniform format (e.g.,
-
Post-Meeting Follow-up Reminder: Set a time-based trigger to run 24 hours after the meeting ends, ensuring timely task completion.
// Pseudo code for the application FUNCTION setFollowUpTrigger(eventId, endTime) CALCULATE FollowUpTime (EndTime + 24 Hrs) CREATE Trigger 'sendActionItemReminder' at FollowUpTime END FUNCTION
3. **Dynamic Template Selection:**
Allow the script to choose a template based on the meeting type (e.g., internal standup vs. client presentation) using multiple calendar tags (e.g., `[INTERNAL_NOTES]`, `[CLIENT_NOTES]`).
### 7. Resources
* [Google Apps Script Documentation: Calendar Service](https://developers.google.com/apps-script/reference/calendar/calendar-app)
* [Google Apps Script Documentation: Document Service](https://developers.google.com/apps-script/reference/document/document-app)
* [Google Apps Script Documentation: Drive Service](https://developers.google.com/apps-script/reference/drive/drive-app)
* [Guide to Setting Up Time-Driven Triggers in GAS](https://developers.google.com/apps-script/guides/triggers/time-driven)
***
## Ready to deploy this system?
This is not a theoretical concept; it is a deployed solution that saves our clients thousands of dollars annually in administrative overhead and drastically improves project accountability.
We deliver specific, battle-tested products, not generalized consulting. If your agency is ready to save 5+ hours weekly and enforce documentation consistency,
**Book a 30-minute call.** We'll review your identify integration points, and scope the work. Just click on the button below and fill the form to help us get started.
Need a Custom Automation Solution?
We specialize in building tailored Google Workspace automations for businesses of all sizes. Let us help you eliminate repetitive tasks and streamline your workflows.